 Image credit: Hyungjin Chung
Image credit: Hyungjin ChungAbstract
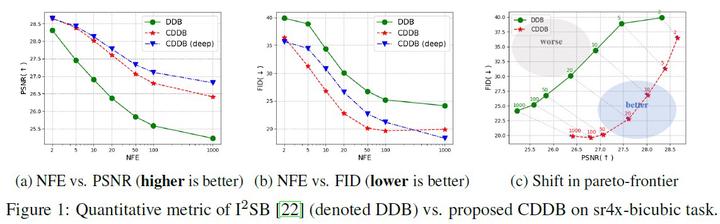
Diffusion model-based inverse problem solvers have shown impressive performance, but are limited in speed, mostly as they require reverse diffusion sampling starting from noise. Several recent works have tried to alleviate this problem by building a diffusion process, directly bridging the clean and the corrupted for specific inverse problems. To provide a coherent explanation of the seemingly different approaches, we first develop a unified framework under the name Direct Diffusion Bridges (DDB), showing that while motivated by different theories, the resulting algorithms only differ in the choice of parameters. Then, we highlight a critical limitation of the current DDB framework, namely that it does not ensure data consistency. To address this problem, we propose a modified inference procedure that imposes data consistency without the need for fine-tuning. We term the resulting method data Consistent DDB (CDDB), which outperforms its inconsistent counterpart in terms of both perception and distortion metrics, thereby effectively pushing the Pareto-frontier toward the optimum. Our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art results on both evaluation criteria, showcasing its superiority over existing methods.